Chemical Datasheet
BIPHENYL |
|
Chemical Identifiers
The
Chemical Identifier fields
include common identification numbers, the
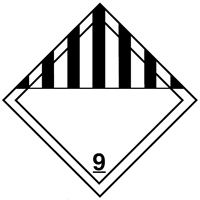
NFPA diamond
U.S. Department of Transportation hazard labels, and a general
description of the chemical. The information in CAMEO Chemicals comes
from a variety of
data sources.
| CAS Number | UN/NA Number | DOT Hazard Label | USCG CHRIS Code |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
||
| NIOSH Pocket Guide | International Chem Safety Card | ||
Diphenyl
|
|||
NFPA 704
| Diamond | Hazard | Value | Description | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
1 | Can cause significant irritation. | |||||||||
|
|
1 | Must be preheated before ignition can occur. | ||||||||||
|
|
0 | Normally stable, even under fire conditions. | ||||||||||
|
|
(NFPA, 2010)
General Description
A clear colorless liquid with a pleasant odor. Flash point 180°F. Insoluble in water. Vapors are heavier than air. Used to manufacture other chemicals and as a fungicide.
Hazards
The
Hazard fields
include
special hazard alerts
air and water
reactions, fire hazards, health hazards, a reactivity profile, and
details about
reactive groups assignments
and
potentially incompatible absorbents.
The information in CAMEO Chemicals comes from a variety of
data sources.
Reactivity Alerts
none
Air & Water Reactions
Insoluble in water.
Fire Hazard
Combustible. Emits toxic fumes under fire conditions. (USCG, 1999)
Health Hazard
CALL FOR MEDICAL AID. VAPOR, MIST OR DUST: Irritating to eyes, nose, throat and skin. Flush affected area with plenty of water. IF IN EYES, hold eyelids open and flush with plenty of water. SOLID OR LIQUID: Irritating to skin and eyes, nose and throat. Remove contaminated clothing and shoes. Flush affected areas with plenty water. IF IN EYES, hold eyelids open and flush with plenty of water. If swallowed, do not induce vomiting. Harmful if inhaled or swallowed. Causes irritation to eyes, skin and mucous membrane and upper respiratory tract. Causes central nervous system depression, paralysis and convulsion in animals. May cause headache, diffuse gastrointestinal pain, nausea, indigestion, numbness and aching of limbs, and general fatigue. Liver function test may show abnormalities. Chronic exposure is mostly characterized by central nervous system symptoms, fatigue, headache, tremor, insomnia, sensory impairment, and mood changes. Such symptoms are rare however. (USCG, 1999)
Reactivity Profile
BIPHENYL is incompatible with oxidizers. (NTP, 1992)
Belongs to the Following Reactive Group(s)
Potentially Incompatible Absorbents
No information available.
Response Recommendations
The
Response Recommendation fields
include isolation and evacuation distances, as well as recommendations for
firefighting, non-fire response, protective clothing, and first aid. The
information in CAMEO Chemicals comes from a variety of
data sources.
Isolation and Evacuation
Excerpt from ERG Guide 171 [Substances (Low to Moderate Hazard)]:
IMMEDIATE PRECAUTIONARY MEASURE: Isolate spill or leak area in all directions for at least 50 meters (150 feet) for liquids and at least 25 meters (75 feet) for solids.
SPILL: Increase the immediate precautionary measure distance, in the downwind direction, as necessary.
FIRE: If tank, rail tank car or highway tank is involved in a fire, ISOLATE for 800 meters (1/2 mile) in all directions; also, consider initial evacuation for 800 meters (1/2 mile) in all directions. (ERG, 2024)
IMMEDIATE PRECAUTIONARY MEASURE: Isolate spill or leak area in all directions for at least 50 meters (150 feet) for liquids and at least 25 meters (75 feet) for solids.
SPILL: Increase the immediate precautionary measure distance, in the downwind direction, as necessary.
FIRE: If tank, rail tank car or highway tank is involved in a fire, ISOLATE for 800 meters (1/2 mile) in all directions; also, consider initial evacuation for 800 meters (1/2 mile) in all directions. (ERG, 2024)
Firefighting
Excerpt from ERG Guide 171 [Substances (Low to Moderate Hazard)]:
CAUTION: Fire involving Safety devices (UN3268) and Fire suppressant dispersing devices (UN3559) may have a delayed activation and a risk of hazardous projectiles. Extinguish the fire at a safe distance.
SMALL FIRE: Dry chemical, CO2, water spray or regular foam.
LARGE FIRE: Water spray, fog or regular foam. Do not scatter spilled material with high-pressure water streams. If it can be done safely, move undamaged containers away from the area around the fire. Dike runoff from fire control for later disposal.
FIRE INVOLVING TANKS: Cool containers with flooding quantities of water until well after fire is out. Withdraw immediately in case of rising sound from venting safety devices or discoloration of tank. ALWAYS stay away from tanks in direct contact with flames. (ERG, 2024)
CAUTION: Fire involving Safety devices (UN3268) and Fire suppressant dispersing devices (UN3559) may have a delayed activation and a risk of hazardous projectiles. Extinguish the fire at a safe distance.
SMALL FIRE: Dry chemical, CO2, water spray or regular foam.
LARGE FIRE: Water spray, fog or regular foam. Do not scatter spilled material with high-pressure water streams. If it can be done safely, move undamaged containers away from the area around the fire. Dike runoff from fire control for later disposal.
FIRE INVOLVING TANKS: Cool containers with flooding quantities of water until well after fire is out. Withdraw immediately in case of rising sound from venting safety devices or discoloration of tank. ALWAYS stay away from tanks in direct contact with flames. (ERG, 2024)
Non-Fire Response
Excerpt from ERG Guide 171 [Substances (Low to Moderate Hazard)]:
Do not touch or walk through spilled material. Stop leak if you can do it without risk. Prevent dust cloud. For Asbestos, avoid inhalation of dust. Cover spill with plastic sheet or tarp to minimize spreading. Do not clean up or dispose of, except under supervision of a specialist.
SMALL DRY SPILL: With clean shovel, place material into clean, dry container and cover loosely; move containers from spill area.
SMALL SPILL: Pick up with sand or other non-combustible absorbent material and place into containers for later disposal.
LARGE SPILL: Dike far ahead of liquid spill for later disposal. Cover powder spill with plastic sheet or tarp to minimize spreading. Prevent entry into waterways, sewers, basements or confined areas. (ERG, 2024)
Do not touch or walk through spilled material. Stop leak if you can do it without risk. Prevent dust cloud. For Asbestos, avoid inhalation of dust. Cover spill with plastic sheet or tarp to minimize spreading. Do not clean up or dispose of, except under supervision of a specialist.
SMALL DRY SPILL: With clean shovel, place material into clean, dry container and cover loosely; move containers from spill area.
SMALL SPILL: Pick up with sand or other non-combustible absorbent material and place into containers for later disposal.
LARGE SPILL: Dike far ahead of liquid spill for later disposal. Cover powder spill with plastic sheet or tarp to minimize spreading. Prevent entry into waterways, sewers, basements or confined areas. (ERG, 2024)
Protective Clothing
Excerpt from NIOSH Pocket Guide for Diphenyl :
:
Skin: PREVENT SKIN CONTACT - Wear appropriate personal protective clothing to prevent skin contact.
Eyes: PREVENT EYE CONTACT - Wear appropriate eye protection to prevent eye contact.
Wash skin: WHEN CONTAMINATED - The worker should immediately wash the skin when it becomes contaminated.
Remove: WHEN WET OR CONTAMINATED - Work clothing that becomes wet or significantly contaminated should be removed and replaced.
Change: DAILY - Workers whose clothing may have become contaminated should change into uncontaminated clothing before leaving the work premises.
Provide:
• EYEWASH (MOLT) - Eyewash fountains should be provided (when this chemical is in molten form) in areas where there is any possibility that workers could be exposed to the substances; this is irrespective of the recommendation involving the wearing of eye protection.
• QUICK DRENCH (MOLT) - Facilities for quickly drenching the body should be provided (when this chemical is in molten form) within the immediate work area for emergency use where there is a possibility of exposure. [Note: It is intended that these facilities provide a sufficient quantity or flow of water to quickly remove the substance from any body areas likely to be exposed. The actual determination of what constitutes an adequate quick drench facility depends on the specific circumstances. In certain instances, a deluge shower should be readily available, whereas in others, the availability of water from a sink or hose could be considered adequate.] (NIOSH, 2024)
 :
:Skin: PREVENT SKIN CONTACT - Wear appropriate personal protective clothing to prevent skin contact.
Eyes: PREVENT EYE CONTACT - Wear appropriate eye protection to prevent eye contact.
Wash skin: WHEN CONTAMINATED - The worker should immediately wash the skin when it becomes contaminated.
Remove: WHEN WET OR CONTAMINATED - Work clothing that becomes wet or significantly contaminated should be removed and replaced.
Change: DAILY - Workers whose clothing may have become contaminated should change into uncontaminated clothing before leaving the work premises.
Provide:
• EYEWASH (MOLT) - Eyewash fountains should be provided (when this chemical is in molten form) in areas where there is any possibility that workers could be exposed to the substances; this is irrespective of the recommendation involving the wearing of eye protection.
• QUICK DRENCH (MOLT) - Facilities for quickly drenching the body should be provided (when this chemical is in molten form) within the immediate work area for emergency use where there is a possibility of exposure. [Note: It is intended that these facilities provide a sufficient quantity or flow of water to quickly remove the substance from any body areas likely to be exposed. The actual determination of what constitutes an adequate quick drench facility depends on the specific circumstances. In certain instances, a deluge shower should be readily available, whereas in others, the availability of water from a sink or hose could be considered adequate.] (NIOSH, 2024)
DuPont Tychem® Suit Fabrics
No information available.
First Aid
EYES: First check the victim for contact lenses and remove if present. Flush victim's eyes with water or normal saline solution for 20 to 30 minutes while simultaneously calling a hospital or poison control center. Do not put any ointments, oils, or medication in the victim's eyes without specific instructions from a physician. IMMEDIATELY transport the victim after flushing eyes to a hospital even if no symptoms (such as redness or irritation) develop.
SKIN: IMMEDIATELY flood affected skin with water while removing and isolating all contaminated clothing. Gently wash all affected skin areas thoroughly with soap and water. If symptoms such as redness or irritation develop, IMMEDIATELY call a physician and be prepared to transport the victim to a hospital for treatment.
INHALATION: IMMEDIATELY leave the contaminated area; take deep breaths of fresh air. If symptoms (such as wheezing, coughing, shortness of breath, or burning in the mouth, throat, or chest) develop, call a physician and be prepared to transport the victim to a hospital. Provide proper respiratory protection to rescuers entering an unknown atmosphere. Whenever possible, Self-Contained Breathing Apparatus (SCBA) should be used; if not available, use a level of protection greater than or equal to that advised under Protective Clothing.
INGESTION: DO NOT INDUCE VOMITING. If the victim is conscious and not convulsing, give 1 or 2 glasses of water to dilute the chemical and IMMEDIATELY call a hospital or poison control center. Be prepared to transport the victim to a hospital if advised by a physician. If the victim is convulsing or unconscious, do not give anything by mouth, ensure that the victim's airway is open and lay the victim on his/her side with the head lower than the body. DO NOT INDUCE VOMITING. IMMEDIATELY transport the victim to a hospital. (NTP, 1992)
SKIN: IMMEDIATELY flood affected skin with water while removing and isolating all contaminated clothing. Gently wash all affected skin areas thoroughly with soap and water. If symptoms such as redness or irritation develop, IMMEDIATELY call a physician and be prepared to transport the victim to a hospital for treatment.
INHALATION: IMMEDIATELY leave the contaminated area; take deep breaths of fresh air. If symptoms (such as wheezing, coughing, shortness of breath, or burning in the mouth, throat, or chest) develop, call a physician and be prepared to transport the victim to a hospital. Provide proper respiratory protection to rescuers entering an unknown atmosphere. Whenever possible, Self-Contained Breathing Apparatus (SCBA) should be used; if not available, use a level of protection greater than or equal to that advised under Protective Clothing.
INGESTION: DO NOT INDUCE VOMITING. If the victim is conscious and not convulsing, give 1 or 2 glasses of water to dilute the chemical and IMMEDIATELY call a hospital or poison control center. Be prepared to transport the victim to a hospital if advised by a physician. If the victim is convulsing or unconscious, do not give anything by mouth, ensure that the victim's airway is open and lay the victim on his/her side with the head lower than the body. DO NOT INDUCE VOMITING. IMMEDIATELY transport the victim to a hospital. (NTP, 1992)
Physical Properties
The
Physical Property fields
include properties such as vapor pressure and
boiling point, as well as explosive limits and
toxic exposure thresholds
The information in CAMEO Chemicals comes from a variety of
data sources.
Note: For Vapor Density and Specific Gravity, comparing the value to 1.0 can tell you if the chemical will likely sink/rise in air or sink/float in fresh water (respectively). Short phrases have been added to those values below as an aid. However, make sure to also consider the circumstances of a release. The Vapor Density comparisons are only valid when the gas escaping is at the same temperature as the surrounding air itself. If the chemical is escaping from a container where it was pressurized or refrigerated, it may first escape and behave as a heavy gas and sink in the air (even if it has a Vapor Density value less than 1). Also, the Specific Gravity comparisons are for fresh water (density 1.0 g/mL). If your spill is in salt water (density about 1.027 g/mL), you need to adjust the point of comparison. There are some chemicals that will sink in fresh water and float in salt water.
Note: For Vapor Density and Specific Gravity, comparing the value to 1.0 can tell you if the chemical will likely sink/rise in air or sink/float in fresh water (respectively). Short phrases have been added to those values below as an aid. However, make sure to also consider the circumstances of a release. The Vapor Density comparisons are only valid when the gas escaping is at the same temperature as the surrounding air itself. If the chemical is escaping from a container where it was pressurized or refrigerated, it may first escape and behave as a heavy gas and sink in the air (even if it has a Vapor Density value less than 1). Also, the Specific Gravity comparisons are for fresh water (density 1.0 g/mL). If your spill is in salt water (density about 1.027 g/mL), you need to adjust the point of comparison. There are some chemicals that will sink in fresh water and float in salt water.
| Chemical Formula: |
|
Flash Point:
235°F
(NTP, 1992)
Lower Explosive Limit (LEL):
0.6 %
at 232°F
(USCG, 1999)
Upper Explosive Limit (UEL):
5.8 %
at 331°F.
(USCG, 1999)
Autoignition Temperature:
1004°F
(USCG, 1999)
Melting Point:
156 to 160°F
(NTP, 1992)
Vapor Pressure:
0.005 mmHg
(NIOSH, 2024)
Vapor Density (Relative to Air):
5.31
(USCG, 1999)
- Heavier than air; will sink
Specific Gravity:
0.992
at 68°F
(USCG, 1999)
- Less dense than water; will float
Boiling Point:
489 to 491°F
at 760 mmHg
(NTP, 1992)
Molecular Weight:
154.22
(NTP, 1992)
Water Solubility:
Insoluble
(NTP, 1992)
Ionization Energy/Potential:
7.95 eV
(NIOSH, 2024)
IDLH:
100 mg/m3
(NIOSH, 2024)
AEGLs (Acute Exposure Guideline Levels)
| Exposure Period | AEGL-1 | AEGL-2 | AEGL-3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 minutes | NR | 12 ppm | NR |
| 30 minutes | NR | 12 ppm | NR |
| 60 minutes | NR | 9.6 ppm | NR |
| 4 hours | NR | 6 ppm | NR |
| 8 hours | NR | 4.4 ppm | NR |
NR = Not recommended due to insufficient data
(NAC/NRC, 2024)
ERPGs (Emergency Response Planning Guidelines)
No ERPG information available.PACs (Protective Action Criteria)
| Chemical | PAC-1 | PAC-2 | PAC-3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diphenyl; (Biphenyl) (92-52-4) | 0.87 ppm | 9.6 ppm | 300 ppm | LEL = 6000 ppm |
(DOE, 2024)
Regulatory Information
The
Regulatory Information fields
include information from
the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency's Title III Consolidated List of
Lists,
the U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency's Chemical Facility
Anti-Terrorism Standards,
and the U.S. Occupational Safety and Health Administration's
Process Safety Management of Highly Hazardous Chemicals Standard List
(see more about these
data sources).
EPA Consolidated List of Lists
| Regulatory Name | CAS Number/ 313 Category Code |
EPCRA 302 EHS TPQ |
EPCRA 304 EHS RQ |
CERCLA RQ | EPCRA 313 TRI |
RCRA Code |
CAA 112(r) RMP TQ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Biphenyl | 92-52-4 | 100 pounds | 313 |
(EPA List of Lists, 2024)
CISA Chemical Facility Anti-Terrorism Standards (CFATS)
No regulatory information available.OSHA Process Safety Management (PSM) Standard List
No regulatory information available.Alternate Chemical Names
This section provides a listing of alternate names for this chemical,
including trade names and synonyms.
- BIBENZENE
- BIPHENYL
- 1,1'-BIPHENYL
- CAROLID AL
- DIPHENYL
- 1,1'-DIPHENYL
- LEMONENE
- PHENADOR-X
- PHENYL BENZENE
- PHENYLBENZENE
- PHPH
- TETROSIN LY
- XENENE