
 Print
Print
Chemical Datasheet
CREOSOTE, [COAL TAR] |
|
Chemical Identifiers
| CAS Number |
UN/NA Number |
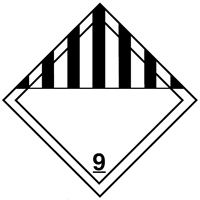
DOT Hazard Label |
USCG CHRIS Code |
|
|
|
|
|
| NIOSH Pocket Guide |
International Chem Safety Card |
|
none
|
|
NFPA 704
General Description
This material contains creosote, an EPA designated hazardous substance. It often contains substantial amounts of naphthalene and anthracene. The primary hazard is the threat posed to the environment. Immediate steps should be taken to limit its spread to the environment. Since it is a liquid it can easily penetrate the soil and contaminate groundwater and nearby streams.
Hazards
Reactivity Alerts
none
Air & Water Reactions
This chemical may be air sensitive. Insoluble in water.
Fire Hazard
Behavior in Fire: Heavy, irritating black smoke is formed. (USCG, 1999)
Health Hazard
Vapors cause moderate irritation of nose and throat. Liquid causes severe burns of eyes and reddening and itching of skin. Prolonged contact with skin can cause burns. Ingestion causes salivation, vomiting, respiratory difficulties, thready pulse, vertigo, headache, loss of pupillary reflexes, hypothermia, cyanosis, mild convulsions. (USCG, 1999)
Reactivity Profile
Phenols, such as CREOSOTE, do not behave as organic alcohols, as one might guess from the presence of a hydroxyl (-OH) group in their structure. Instead, they react as weak organic acids. Phenols and cresols are much weaker as acids than common carboxylic acids (phenol has pKa = 9.88). These materials are incompatible with strong reducing substances such as hydrides, nitrides, alkali metals, and sulfides. Flammable gas (H2) is often generated, and the heat of the reaction may ignite the gas. Heat is also generated by the acid-base reaction between phenols and bases. Such heating may initiate polymerization of the organic compound. Phenols are sulfonated very readily (for example, by concentrated sulfuric acid at room temperature). The reactions generate heat. Phenols are also nitrated very rapidly, even by dilute nitric acid. This compound is incompatible with strong oxidizers. (NTP, 1992)
Belongs to the Following Reactive Group(s)
Potentially Incompatible Absorbents
No information available.
Response Recommendations
Isolation and Evacuation
Excerpt from ERG Guide 171 [Substances (Low to Moderate Hazard)]:
IMMEDIATE PRECAUTIONARY MEASURE: Isolate spill or leak area in all directions for at least 50 meters (150 feet) for liquids and at least 25 meters (75 feet) for solids.
SPILL: Increase the immediate precautionary measure distance, in the downwind direction, as necessary.
FIRE: If tank, rail tank car or highway tank is involved in a fire, ISOLATE for 800 meters (1/2 mile) in all directions; also, consider initial evacuation for 800 meters (1/2 mile) in all directions. (ERG, 2024)
Firefighting
Excerpt from ERG Guide 171 [Substances (Low to Moderate Hazard)]:
CAUTION: Fire involving Safety devices (UN3268) and Fire suppressant dispersing devices (UN3559) may have a delayed activation and a risk of hazardous projectiles. Extinguish the fire at a safe distance.
SMALL FIRE: Dry chemical, CO2, water spray or regular foam.
LARGE FIRE: Water spray, fog or regular foam. Do not scatter spilled material with high-pressure water streams. If it can be done safely, move undamaged containers away from the area around the fire. Dike runoff from fire control for later disposal.
FIRE INVOLVING TANKS: Cool containers with flooding quantities of water until well after fire is out. Withdraw immediately in case of rising sound from venting safety devices or discoloration of tank. ALWAYS stay away from tanks in direct contact with flames. (ERG, 2024)
Non-Fire Response
Excerpt from ERG Guide 171 [Substances (Low to Moderate Hazard)]:
Do not touch or walk through spilled material. Stop leak if you can do it without risk. Prevent dust cloud. For Asbestos, avoid inhalation of dust. Cover spill with plastic sheet or tarp to minimize spreading. Do not clean up or dispose of, except under supervision of a specialist.
SMALL DRY SPILL: With clean shovel, place material into clean, dry container and cover loosely; move containers from spill area.
SMALL SPILL: Pick up with sand or other non-combustible absorbent material and place into containers for later disposal.
LARGE SPILL: Dike far ahead of liquid spill for later disposal. Cover powder spill with plastic sheet or tarp to minimize spreading. Prevent entry into waterways, sewers, basements or confined areas. (ERG, 2024)
Protective Clothing
All-service canister mask; rubber gloves; chemical safety goggles and/or face shield; overalls or a neoprene apron; barrier creams. (USCG, 1999)
DuPont Tychem® Suit Fabrics
Normalized Breakthrough Times (in Minutes)
| Chemical |
CAS Number |
State |
QS |
QC |
SL |
C3 |
TF |
TP |
RC |
TK |
RF |
| Creosote |
8001-58-9 |
Liquid |
|
|
|
|
>480 |
>480 |
|
|
|
Special Warning from DuPont: Tychem® and Tyvek® fabrics should not be
used around heat, flames, sparks or in potentially flammable or
explosive environments. Only...
(DuPont, 2024)
First Aid
EYES: First check the victim for contact lenses and remove if present. Flush victim's eyes with water or normal saline solution for 20 to 30 minutes while simultaneously calling a hospital or poison control center. Do not put any ointments, oils, or medication in the victim's eyes without specific instructions from a physician. IMMEDIATELY transport the victim after flushing eyes to a hospital even if no symptoms (such as redness or irritation) develop.
SKIN: IMMEDIATELY flood affected skin with water while removing and isolating all contaminated clothing. Gently wash all affected skin areas thoroughly with soap and water. IMMEDIATELY call a hospital or poison control center even if no symptoms (such as redness or irritation) develop. IMMEDIATELY transport the victim to a hospital for treatment after washing the affected areas.
INHALATION: IMMEDIATELY leave the contaminated area; take deep breaths of fresh air. IMMEDIATELY call a physician and be prepared to transport the victim to a hospital even if no symptoms (such as wheezing, coughing, shortness of breath, or burning in the mouth, throat, or chest) develop. Provide proper respiratory protection to rescuers entering an unknown atmosphere. Whenever possible, Self-Contained Breathing Apparatus (SCBA) should be used; if not available, use a level of protection greater than or equal to that advised under Protective Clothing.
INGESTION: DO NOT INDUCE VOMITING. If the victim is conscious and not convulsing, give 1 or 2 glasses of water to dilute the chemical and IMMEDIATELY call a hospital or poison control center. Be prepared to transport the victim to a hospital if advised by a physician. If the victim is convulsing or unconscious, do not give anything by mouth, ensure that the victim's airway is open and lay the victim on his/her side with the head lower than the body. DO NOT INDUCE VOMITING. IMMEDIATELY transport the victim to a hospital.
OTHER: Since this chemical is a known or suspected carcinogen you should contact a physician for advice regarding the possible long term health effects and potential recommendation for medical monitoring. Recommendations from the physician will depend upon the specific compound, its chemical, physical and toxicity properties, the exposure level, length of exposure, and the route of exposure. (NTP, 1992)
Physical Properties
Chemical Formula:
data unavailable
Flash Point:
165°F
(NTP, 1992)
Lower Explosive Limit (LEL): data unavailable
Upper Explosive Limit (UEL): data unavailable
Autoignition Temperature:
637°F
(USCG, 1999)
Melting Point:
Varies
(NTP, 1992)
Vapor Pressure:
42 mmHg
at 72°F
; 64 mmHg at 124°F; 86 mmHg at 167°F
(NTP, 1992)
Vapor Density (Relative to Air): data unavailable
Specific Gravity:
1.05 to 1.09
at 59°F
(USCG, 1999)
Boiling Point:
397°F
at 760 mmHg
(NTP, 1992)
Molecular Weight:
Varies
(NTP, 1992)
Water Solubility:
less than 1 mg/mL
at 70.7°F
(NTP, 1992)
Ionization Energy/Potential: data unavailable
IDLH: data unavailable
AEGLs (Acute Exposure Guideline Levels)
No AEGL information available.
ERPGs (Emergency Response Planning Guidelines)
No ERPG information available.
PACs (Protective Action Criteria)
| Chemical |
PAC-1 |
PAC-2 |
PAC-3 |
| Creosote (coal tar) (8001-58-9)
|
0.6 mg/m3 |
120 mg/m3 |
700 mg/m3 |
(DOE, 2024)
Regulatory Information
EPA Consolidated List of Lists
| Regulatory Name |
CAS Number/
313 Category Code |
EPCRA 302
EHS TPQ |
EPCRA 304
EHS RQ |
CERCLA RQ |
EPCRA 313
TRI |
RCRA
Code |
CAA 112(r)
RMP TQ |
| Creosote |
8001-58-9 |
|
|
|
313 |
|
|
| Creosote |
N.A. |
|
|
1 pound |
|
U051 |
|
(EPA List of Lists, 2024)
CISA Chemical Facility Anti-Terrorism Standards (CFATS)
No regulatory information available.
OSHA Process Safety Management (PSM) Standard List
No regulatory information available.
Alternate Chemical Names
- AWPA #1
- BRICK OIL
- COAL CREOSOTE
- COAL TAR CREOSOTE
- CREOSOTE
- CREOSOTE (WOOD)
- CREOSOTE OIL
- CREOSOTE P1
- CREOSOTE, COAL TAR
- CREOSOTE, FROM COAL TAR
- CREOSOTE, [COAL TAR]
- CREOSOTUM
- CRESYLIC CREOSOTE
- DEAD OIL
- HEAVY OIL
- LIQUID PITCH OIL
- NAPHTHALENE OIL
- PRESERV-O-SOTE
- SAKRESOTE 100
- TAR OIL
- WASH OIL


 Print
Print
